

NAVSTAR
The primary set of satellites, or constellation, used for GPS
systems is known as Navigation Satellite Timing and Ranging or
NAVSTAR. NAVSTAR was developed by the United States Department
of Defense, and the first satellite was launched in the late 1980s.
The NAVSTAR Constellation was designed to operate with a minimum
of 24 satellites, but with room for expansion up to 32 satellites.
There are currently 29 operational satellites in the NAVSTAR constellation.
These satellites are arranged in 6 orbital planes, which are inclined
to the Earth’s equator at 55 degrees, and a height of 20,200
km. Within these orbital planes, the satellites make an orbit
approximately every 12 hours.
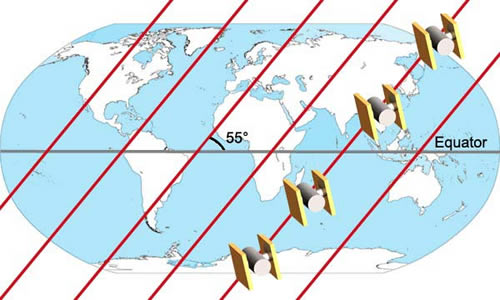
NAVSTAR Orbital Planes
Global Navigation Satellite Systems
In addition to the NAVSTAR Constellation, there are several
other navigational satellite systems. Together, all of these systems
in combination with GPS, are referred to as Global Navigation
Satellite Systems (GNSS).
Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
- Developed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for
aviation use, but is generally available
- Europe and Asia have equivalent systems, EGNOS and MSAS,
respectively.
GLONASS
- Russian GPS equivalent.
- Due to economic problems the future is of GLONASS is uncertain.
Galileo
- Satellite navigation system under development by the European
Union.
- Intended to be a global system.
- Better coverage of higher latitudes.
- Fully compatible with GPS.
Top of Page
Global Positioning Systems : Next >>
GPS Satellites
